GE CMS FTP¶
Sensors¶
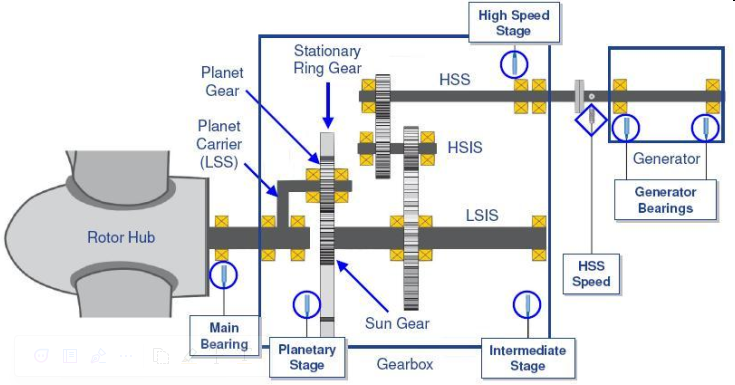
Echoenergia 1.X wind turbines are equipped with the Bently Nevada 3701 condition monitoring system. It has 6 accelerometers positioned as shown in the image below.
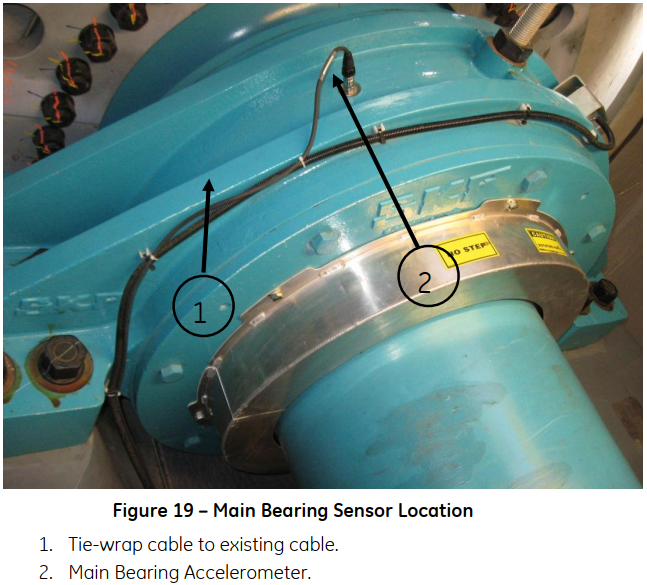
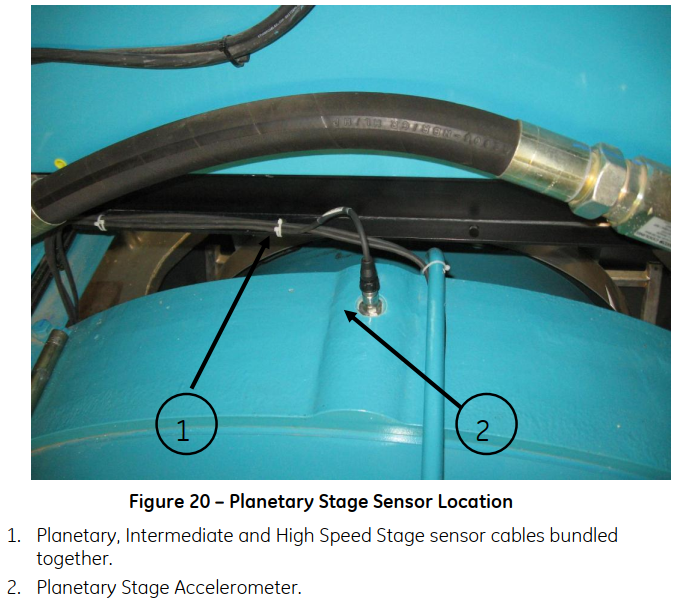
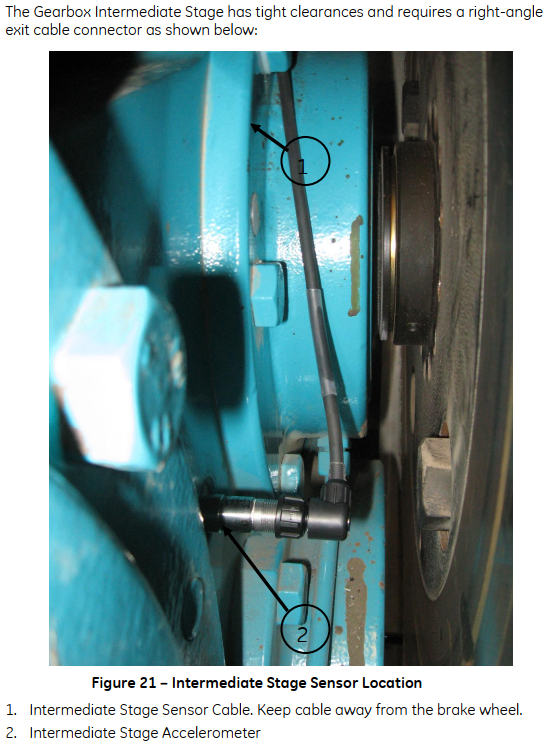
For a more detailed view on the sensors, the following images show them installed in a real wind turbine. These images were extracted from the Bently 3701 operations and maintenance manual saved in the Performance Sharepoint.
-
Main Bearing
-
Gearbox Planetary Stage
-
Gearbox Intermediate Stage
-
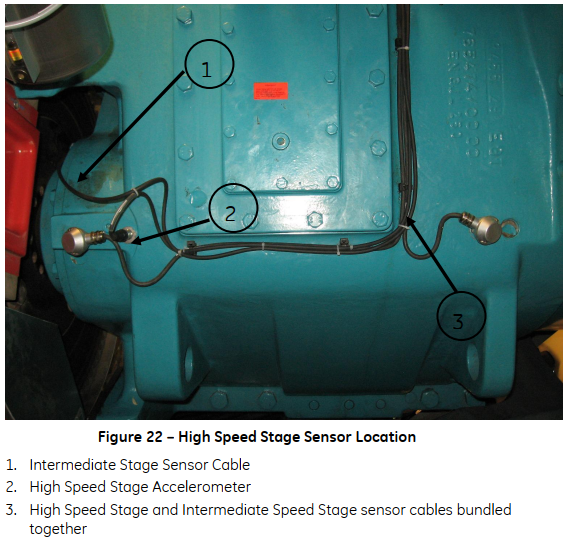
Gearbox High Speed Stage
-
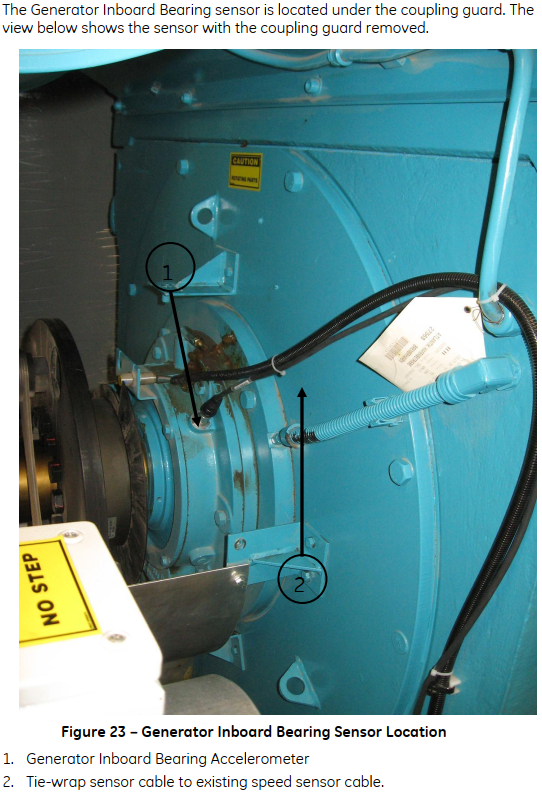
Generator Drive End
-
Generator Non-Drive End
Data¶
The Bently CMS equipment in our GE wind farms collects Static and Dynamic data. Dynamic data is collected every four hours and Static data is collected every 10 minutes. This data is stored in the server using GE's proprietary Proficy Historian.
Waveforms are acquired in two different ways: synchronously or asynchronously.
- Synchronous: Considers the rotation speed of the shaft so that every waveform collected represents 1, 2, 3... rotations of the shaft, regardless of its speed.
- Asynchronous: Waveform collected at the same frequency all the times. This will result in waveforms that represent partial rotation cycles.
Below, the number of samples and resolutions for each sensor are described:
- Asynchronous Waveform: 8192 samples, 320 ms
- Synchronous Waveform: 8192 samples
- 4 revolutions, 2048 samples/rev
- 8 revolutions, 1024 samples/rev
- 16 revolutions, 512 samples/rev
- 32 revolutions, 256 samples/rev
- 64 revolutions, 128 samples/rev
- Spectrums:
- Main Bearing:
- 8 revolutions, 1024 samples/rev
- 3200 lines Sync Enveloped
- Gearbox stages:
- 3200 lines Sync Enveloped
- 3200 lines Sync High Res
- Number of revolutions and samples per revolution vary based on the selected asset
- Generator
- 64 revolutions, 128 samples/rev
- 3200 lines Sync Enveloped
- 3200 lines Sync High Res
- Tower Sway
- 15.625 Hz, 200 lines
- Main Bearing:
Data Access¶
OPC DA¶
The Farm Client has an OPC DA server which can be used to retrieve data from the farm client. It is available under the name Bently Nevada OPC DA Server V1 and has all static data available.
There are two main problems with using this OPC DA server:
- The data available is not real time, but 10 minute resolution. Using OPC to get this type of data is far from ideal, as if we lose the connection we'll not be able to retrieve historical data.
- The OPC server has a lot of points, and tests made with Bazefield proved that it is not reliable. When trying to get data for all the turbines, the server just did not respond, resulting in a lot of data gaps.
Considering the above, OPC DA was discarded as a reliable option to retrieve historical data.
SQL¶
Proficy Historian has a SQL like query interface that allows us to retrieve data from it. The documentation of this interface can be found here and in the CMS server test queries can be executed using the Historian Interactive SQL application, which is just a console where we can execute SQL commands to the historian.
Initial tests using this SQL interface showed that we can reliably retrieve all historical data available with it. Unfortunately, there were two main points that stopped us from using it:
- We could not connect to the historian using Python or any other SQL administration program. The only way the connection worked was through the
Historian Interactive SQLapplication, which does not solve our problem. Maybe with further investigation this could be solved, but not much time was spent here. - When trying to get data for many tags or assets the queries just hang up, being stuck for several minutes. As the goal was to retrieve all data, this was a main problem.
Again, considering the points above, SQL interface was discarded.
Farm Client Export¶
The most straightforward option to reliably get CMS data was to directly open the Farm Client in the CMS server and use its built in export functionality, which will create a CSV file with all the requested data.
The problem with this solution is that this export functionality is not available through any APIs, but only through the GUI of the Farm Client. This imposes a couple problems:
- Interacting with GUI programs is hard to do as you have to mimic mouse movement or keyboard presses to achieve your desired goal.
- GUI interfaces can only be accessed on Windows with a logged user, which is not the case when we are using a remote desktop connection that will log off when closing it.
Considering that all other possibilities were discarded, we invested some time to find solutions for the two problems above. For the first one we found a chain of keyboard commands that led to the export window and from there it was easy to fill the dates, select the turbines and export the data. For the second one, we found out that installing rdpwrap will increase the number of simultaneous connections to 15 and allow for localhost connection, this way we can open a remote connection to the local server which will force the GUI to say open.
Considering that rdpwrap is needed, please make sure it is installed following the steps described in its GitHub repository. In a simple way, the steps that need to be done are:
- Download the latest installer of
rdwrapfrom the release page. Please download the zip file. - Export the contents of the folder to a desktop folder
- Install the program using the
install.batfile. - Check if it is working using
RDPConf.exe.
After rdpwrap is installed, we need to open a remote connection to the server itself but for another user. Doing this, we make sure that this second connection GUI is kept alive even if the first connection is closed. Usually an RDP icon to connect using user bazefield2 will be saved in the desktop, but if not, connect to localhost with user bazefield2 and password bazefield. Once this is done, you just leave the window open and you can close the first RDP session to the server, the scheduled job will run as expected.
One important point here is to make sure Group Policy settings do not force log off of disconnected sessions. To make sure this is correct go to the path below and make sure the settings are correct, without time limits.
- Run
gpedit.msc→ Navigate to Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates → Windows Components → Remote Desktop Services → Remote Desktop Session Host → Session Time Limits.
Debug¶
In case data is not being exported correctly (Airflow DAG is failing for all wind turbines of one site), you should check the following:
- Access the server remotely and check if the RDP window to localhost using user bazefield2 is open. In case it's not, just reconnect using the RDP icon in the desktop and wait for the next day.
- Are all the items below configured correctly? If not, probably the server was formatted and all needs to be configured again.
- Can you manually export data from Farm Client?
- Task for exporting data configured in task scheduler for every day with program/script
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exeand arguments-command python f:/echo_cms/ge_cms_exporter.py - Python installed.
Pyautoguilibrary installed in Python.- Folder
f:\echo_cmscontains all the scripts? - Folder
f:\echo_cms\_vibrationexists? - Is the
FilleZillaserver installed and running?
FTP Server¶
An FTP server was configured in each GE CMS server to allow for remote access to the exported files and folders. This was done using FileZilla which is an open source FTP server.
To configure the FTP server, you need to open FileZilla Administration Interface in the server and connect using the credentials below.
- Port for admin interface: 14148
- Admin password: pErformance@
The definition of users allowed for remote access is done in the Rights Management -> Users section. By default, we created a performance user using the same password above and a native path F:/echo_cms was mapped to the virtual path /echo_cms. This will make the echo_cms folder available at the root when connecting to the FTP server using the performance user.
Scripts¶
The script used to import data from the FTP server is located in this package and it's description and source code can be found below.
Note
The importer_ge_cms_ftp method is called periodically by an Airflow DAG to import data from the FTP server automatically. Check Airflow for more information on the task and its schedule.
importer_ge_cms_ftp(objects=None, max_tries=3, **kwargs)
¶
Method used to import CMS files from FTP server running in GE CMS server. This also assumes that the files are being correctly exported from the Bently Nevada Farm Client using the GE CMS Exporter script.
This script requires the following definitions in the performance database:
-
Data source of type "ftp_ge_cms" with the following attributes:
1.1 host_address: IP address of the FTP server
1.2 user: username to connect to the FTP server
1.3 password: password to connect to the FTP server
1.4 ftp_folder: folder in the FTP server where the files are located
-
Object with the following attributes:
2.1 manufacturer_name: manufacturer name of the object
-
Connection between the data source and the object
-
Raw data definitions for each type of raw data that will be imported. The name of the raw data definition must be in the format "ge_cms_{raw_data_name}" where raw_data_name is the name of the raw data as it appears in the file name.
-
Features definitions for the model of each object that will be imported. The data_source_type_name must be "ftp_ge_cms" and the name_in_data_source must be the name of the column in the static data file that will be imported.
The script will do the following:
-
Connect to the performance database and get the list of data sources of type "ftp_ge_cms".
-
For each data source, it will connect to the FTP server and get the list of files in the folder.
-
For each object connected to the data source, it will get the list of files that start with the manufacturer_name of the object.
-
For the files of the object, it will get the periods that define an export.
-
For each period, it will get the static data and raw data files.
-
It will read the static data and upload it to Bazefield.
-
It will read the raw data and upload it to the performance database.
-
It will delete the files from the FTP server.
-
Errors will be raised and saved to the ErrorSummary object that will be returned.
Note: All files in the FTP server will be processed. If everything is correct, at the end of the process no files will be left in the FTP server.
Parameters:
-
(objects¶list[str] | None, default:None) –List of desired objects to import data. Set to None to import all. By default None
-
(max_tries¶int, default:3) –Number of tries when connecting to data source and copying files, by default 3
Returns:
-
ErrorSummary–Object containing summary of all errors that occurred during the import process.
Source code in echo_cms/ge_cms_ftp.py
def importer_ge_cms_ftp(
objects: list[str] | None = None,
max_tries: int = 3,
**kwargs, # noqa
) -> ErrorSummary:
"""Method used to import CMS files from FTP server running in GE CMS server. This also assumes that the files are being correctly exported from the Bently Nevada Farm Client using the GE CMS Exporter script.
This script requires the following definitions in the performance database:
1. Data source of type "ftp_ge_cms" with the following attributes:
1.1 host_address: IP address of the FTP server
1.2 user: username to connect to the FTP server
1.3 password: password to connect to the FTP server
1.4 ftp_folder: folder in the FTP server where the files are located
2. Object with the following attributes:
2.1 manufacturer_name: manufacturer name of the object
3. Connection between the data source and the object
4. Raw data definitions for each type of raw data that will be imported. The name of the raw data definition must be in the format "ge_cms_{raw_data_name}" where raw_data_name is the name of the raw data as it appears in the file name.
5. Features definitions for the model of each object that will be imported. The data_source_type_name must be "ftp_ge_cms" and the name_in_data_source must be the name of the column in the static data file that will be imported.
The script will do the following:
1. Connect to the performance database and get the list of data sources of type "ftp_ge_cms".
2. For each data source, it will connect to the FTP server and get the list of files in the folder.
3. For each object connected to the data source, it will get the list of files that start with the manufacturer_name of the object.
4. For the files of the object, it will get the periods that define an export.
5. For each period, it will get the static data and raw data files.
6. It will read the static data and upload it to Bazefield.
7. It will read the raw data and upload it to the performance database.
8. It will delete the files from the FTP server.
9. Errors will be raised and saved to the ErrorSummary object that will be returned.
Note: All files in the FTP server will be processed. If everything is correct, at the end of the process no files will be left in the FTP server.
Parameters
----------
objects : list[str] | None, optional
List of desired objects to import data. Set to None to import all. By default None
max_tries : int, optional
Number of tries when connecting to data source and copying files, by default 3
Returns
-------
ErrorSummary
Object containing summary of all errors that occurred during the import process.
"""
# checking inputs
if objects is None:
objects = []
if not isinstance(objects, list):
raise TypeError(f"objects must be a list of strings, not {type(objects)}")
if not all(isinstance(obj, str) for obj in objects):
raise TypeError("objects must be a list of strings")
if not isinstance(max_tries, int):
raise TypeError(f"max_tries must be an integer, not {type(max_tries)}")
# creating ErrorSummary
errs_summary = ErrorSummary(name="importer_ge_cms_ftp")
# creating connection to performance_db
perfdb = PerfDB(application_name="importer_ge_cms_ftp")
# creating connection to Bazefield
baze = Baze()
# creating a temporary directory to store the files
Path("./temp/").mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
# deleting all folders inside temp_dir that are more than 2 days old
for folder in Path("./temp/").iterdir():
if folder.is_dir() and datetime.fromtimestamp(folder.stat().st_ctime) < datetime.now() - timedelta(days=2):
shutil.rmtree(folder, ignore_errors=True)
with TemporaryDirectory(dir="./temp/") as temp_dir:
logger.info(f"Created temporary directory {temp_dir}")
# getting the list of data sources
data_sources: dict[str, dict[str, Any]] = perfdb.datasources.instances.get(
data_source_types_names=["ftp_ge_cms"],
get_attributes=True,
)
logger.info(f"Found data sources: {list(data_sources.keys())}")
# looping through the data sources
for ds_name, ds_attributes in data_sources.items():
logger.info(f"Processing data source {ds_name}")
# creating ErrorDataSource
errs_ds = ErrorDataSource(name=ds_name)
errs_summary = errs_summary.add_child(errs_ds)
try:
# checking if all the necessary attributes are present
required_attrs = ["host_address", "user", "password", "ftp_folder"]
if any(attr not in ds_attributes for attr in required_attrs):
missing_attrs = [attr for attr in required_attrs if attr not in ds_attributes]
raise ValueError(f"Data source {ds_name} is missing attributes: {missing_attrs}")
# checking if there are connected objects
if ds_attributes["object_names"] is None or (
isinstance(ds_attributes["object_names"], list) and len(ds_attributes["object_names"]) == 0
):
continue
# if we specified objects, check if any of them are connected to the data source
if len(objects) > 0 and all(obj not in objects for obj in ds_attributes["object_names"]):
logger.info(
f"No objects to import for data source {ds_name} as of it's connected objects are in the list of desired objects",
)
continue
# connecting to the FTP server
ftp_conn_properties = FtpConnProperties(
host=ds_attributes["host_address"],
user=ds_attributes["user"],
password=ds_attributes["password"],
timeout=180,
)
# defining number of seconds as a random number from 3 to 10 seconds
retry_wait = 3 + secrets.randbelow(8)
ftp_handler = FtpHandler(ftp_conn_properties, max_retries=max_tries, retry_wait_time=retry_wait)
# change_directory
ftp_handler.change_directory(ds_attributes["ftp_folder"])
baset_path = f"{ftp_handler.current_directory()}/"
# checking if last_run.txt exists
files_list = ftp_handler.list_contents()
if "last_run.txt" not in files_list:
raise ValueError("last_run.txt not found in FTP folder, the exporter script may not be running correctly.")
# copying last_run.txt to temp_dir
ftp_handler.get_file(filename="last_run.txt", dest_directory=temp_dir)
# reading last_run.txt to determine the last time the script was run
with Path(temp_dir, "last_run.txt").open("r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
last_run = datetime.strptime(lines[0].split(":", maxsplit=1)[1].strip(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
last_start_day = datetime.strptime(lines[1].split(":", maxsplit=1)[1].strip(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
last_end_day = datetime.strptime(lines[2].split(":", maxsplit=1)[1].strip(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
logger.info(f"last_run.txt found. {last_run=}, {last_start_day=}, {last_end_day=}")
if last_run < datetime.now() - timedelta(days=2):
err_message = f"The last run of the exporter script was more than 2 days ago ({last_run:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}). The script will try to import the data, but it may be incomplete. Check the CMS server ASAP."
logger.error(err_message)
errs_ds = errs_ds.add_exception(RuntimeError(err_message))
ftp_handler.change_directory(f"{baset_path}_vibration/")
# checking if there are files to be copied
files_list = ftp_handler.list_contents()
files_list.sort()
logger.info(f"Found {len(files_list)} files in FTP folder")
if len(files_list) == 0:
# checking if data was already imported
# reading CmsActivePower from Bazefield to check if there is data for the last day
check_period = DateTimeRange(last_end_day - timedelta(days=1), last_end_day)
check_data = baze.points.values.series.get(
points={ds_attributes["object_names"][0]: ["CmsActivePower"]},
period=check_period,
)
if len(check_data) > 0:
logger.info("No files found in FTP folder. Data was already imported.")
continue
raise ValueError(
"No files found in FTP folder. The exporter script may not be running correctly. Check the CMS server ASAP.",
)
# iterating objects
for obj_name in ds_attributes["object_names"]:
# skipping objects that are not in the list
if len(objects) > 0 and obj_name not in objects:
continue
# deleting object folder in temp_dir if it exists
shutil.rmtree(Path(temp_dir) / obj_name, ignore_errors=True)
logger.info(f"Processing object {obj_name} of data source {ds_name}")
# creating ErrorObject
errs_obj = ErrorObject(name=obj_name)
errs_ds = errs_ds.add_child(errs_obj)
try:
# getting object attributes
obj_def: dict[str, dict[str, Any]] = perfdb.objects.instances.get(
object_names=[obj_name],
get_attributes=True,
attribute_names=["manufacturer_name"],
)[obj_name]
# checking if object contains manufacturer_name
if "manufacturer_name" not in obj_def:
raise ValueError(f"Object {obj_name} is missing attribute 'manufacturer_name'")
# checking if there are files to be copied for this object (files starting with the manufacturer_name)
obj_files = [file for file in files_list if file.startswith(obj_def["manufacturer_name"])]
if not obj_files:
# checking if data was already imported
# reading CmsActivePower from Bazefield to check if there is data for the last day
check_period = DateTimeRange(last_end_day - timedelta(days=1), last_end_day)
check_data = baze.points.values.series.get(
points={obj_name: ["CmsActivePower"]},
period=check_period,
)
if len(check_data) > 0:
logger.info("No files found in FTP folder. Data was already imported.")
continue
raise ValueError(f"No files found for object {obj_name}")
logger.info(f"Found {len(obj_files)} files for object {obj_name}")
# creating directory for the object
obj_dir = Path(temp_dir) / obj_name
obj_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
# getting raw data def for this object
raw_data_def = perfdb.rawdata.definitions.get(
object_names=[obj_name],
data_source_types=["ftp_ge_cms"],
output_type="dict",
)[obj_def["object_model_name"]]
# getting all features for this turbine so we can later upload to Bazefield
features_def: pd.DataFrame = perfdb.features.definitions.get(object_names=[obj_name], output_type="DataFrame")
# filtering only to features with data_source_type_name = "ftp_ge_cms"
features_def = features_def[features_def["data_source_type_name"] == "ftp_ge_cms"].copy()
# removing first level of the index
features_def.index = features_def.index.droplevel(0)
# first getting all static data files to get the dates available
static_files = [file for file in obj_files if "static" in file.lower()]
# getting the periods available (split by _ in -3 and -2 that will be start and end dates)
periods_available = [f"{file.split('_')[-2]}_{file.split('_')[-1].split('.')[0]}" for file in static_files]
# iterating each period available
for period in periods_available:
# getting start and end dates
start_date, end_date = period.split("_")
# dates are in the format MMDDYYYYHHMM
period_range = DateTimeRange(start_date, end_date, date_format="%m%d%Y%H%M")
logger.info(f"{obj_name}: Processing period {period_range}")
# getting the files for this period
period_files = [file for file in obj_files if period in file]
# deleting all "waveform" or "DEI" files
not_wanted_files = [file for file in period_files if "waveform" in file.lower() or "dei" in file.lower()]
for not_wanted_file in not_wanted_files:
ftp_handler.delete_file(not_wanted_file)
# first reading static data as it will be used to get metadata as well
static_files = [file for file in period_files if "static" in file.lower()]
raw_files = [
file
for file in period_files
if "static" not in file.lower() and "waveform" not in file.lower() and "dei" not in file.lower()
]
if not static_files or not raw_files:
# deleting all files for this period
for period_file in period_files:
ftp_handler.delete_file(period_file)
continue
if not static_files or len(static_files) > 1:
err_message = f"{obj_name}: Found {len(static_files)} static files for period {period_range}. Expected 1."
logger.error(err_message)
errs_obj = errs_obj.add_exception(ValueError(err_message))
# copying static files to temp_dir
for file in static_files:
ftp_handler.get_file(filename=file, dest_directory=obj_dir)
# checking if file has more than two lines
more_than_2_lines = False
with Path(obj_dir, static_files[0]).open("r") as f:
line_count = 0
for _ in f:
line_count += 1 # noqa
if more_than_2_lines:
break
if line_count > 2:
more_than_2_lines = True
if not more_than_2_lines:
logger.warning(f"{obj_name}: Static file {static_files[0]} has only one line. Deleting file and raw files.")
ftp_handler.delete_file(static_files[0])
for raw_file in raw_files:
ftp_handler.delete_file(raw_file)
continue
# reading static_files
# dates are in the format 4/29/2024 1:55:48 AM
static_df = pd.read_csv(
Path(obj_dir, static_files[0]),
sep=",",
decimal=".",
header=0,
engine="pyarrow",
dtype_backend="pyarrow",
parse_dates=True,
index_col=0,
date_format="%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p",
)
# removing name of turbine from columns
static_df.columns = [col.split("\\", maxsplit=1)[-1] for col in static_df.columns]
# saving static data to Bazefield
baze_static_df = static_df.copy()
baze_static_df.index = baze_static_df.index.astype("datetime64[s]")
# adjusting timestamps to nearest 10 minutes
baze_static_df.index = baze_static_df.index.round("10min")
baze_static_df = baze_static_df.loc[~baze_static_df.index.duplicated(keep="first")]
baze_static_df.columns = [col.replace("\\", " - ") for col in baze_static_df.columns]
if not_wanted_cols := [
col for col in baze_static_df.columns if col not in features_def["name_in_data_source"].to_list()
]:
baze_static_df = baze_static_df.drop(columns=not_wanted_cols)
err_message = f"{obj_name}: Removed columns {not_wanted_cols} from static data as they are not present in the features table."
logger.error(err_message)
errs_obj = errs_obj.add_exception(ValueError(err_message))
baze_static_df = baze_static_df.astype("double[pyarrow]")
# renaming from name_in_data_source to name of feature (index of features_def)
rename_dict = {v: k for k, v in features_def["name_in_data_source"].to_dict().items()}
baze_static_df = baze_static_df.rename(columns=rename_dict)
baze_static_df.index.name = "time"
baze_static_df.columns = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[[obj_name], baze_static_df.columns],
names=["object_name", "feature_name"],
)
# uploading to postgres and Bazefield
perfdb.features.values.series.insert(df=baze_static_df)
# getting only Power, Speed, Mode and Toque
static_df = static_df[[col for col in static_df.columns if "IONet" in col]].copy()
static_df = static_df.rename(
columns={col: col.split("\\", maxsplit=1)[1].replace("External", "") for col in static_df.columns},
)
static_df = static_df.dropna(how="all")
# copying raw data files to temp_dir
# we are ignoring files that contain "static", "waveform" or "DEI" in the name
for file in raw_files:
ftp_handler.get_file(filename=file, dest_directory=obj_dir)
logger.info(f"{obj_name}: Copied file {file} to temp_dir")
if not raw_files:
continue
# finding the file that contains less lines in all raw files
# this file will be the basis for selecting the moment of the day that will be representative of each day as all timestamps in this file are present in all other files
smaller_file = None
smallest_nrows = None
for raw_file in raw_files:
with Path(obj_dir, raw_file).open("r") as f:
row_count = sum(1 for _ in f)
if row_count > 1 and (smaller_file is None or row_count < smallest_nrows):
smaller_file = raw_file
smallest_nrows = row_count
if smaller_file is None:
# no files with data found
# deleting all raw files for this period and moving to the next period
logger.warning(
f"{obj_name}: No raw files with data found for period {period_range}. Deleting all files for this period.",
)
for raw_file in raw_files:
ftp_handler.delete_file(raw_file)
continue
# getting the timestamps in the smaller file
small_raw_df = pd.read_csv(
Path(obj_dir, smaller_file),
sep=",",
decimal=".",
header=None,
engine="pyarrow",
dtype_backend="pyarrow",
parse_dates=True,
index_col=0,
date_format="%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p",
)
# getting list of timestamps
raw_timestamps = small_raw_df.index.tolist()
# getting list of days present in the raw data
raw_days = [ts.date() for ts in raw_timestamps]
raw_days = dict.fromkeys(set(raw_days))
# getting the moment of the day that will be representative of each day
# we will use active power as the metric to select the moment, the moment with the highest active power will be selected
for day in raw_days:
# getting all timestamps for this day
day_timestamps = [ts for ts in raw_timestamps if ts.date() == day]
# getting the active power for each timestamp in this day using nearest lookup
selected_timestamp = None
selected_power = None
# getting a copy of static_df with rows that contain Power
power_df = static_df[["Power"]].dropna().copy()
# checking if there is any Power data in the static data
if power_df.empty:
logger.warning(f"{obj_name}: No Power data found in static data for day {day}. Skipping day.")
raw_days[day] = None
continue
for ts in day_timestamps:
# getting the closest timestamp in the static data
closest_ts = power_df.index[power_df.index.get_indexer([ts], method="nearest")[0]]
# getting the active power for this timestamp
power = power_df.loc[closest_ts, "Power"]
if selected_power is None or power > selected_power:
selected_power = power
selected_timestamp = ts
if selected_timestamp is None:
err_message = f"{obj_name}: Could not find a representative moment for day {day}."
logger.error(err_message)
errs_obj = errs_obj.add_exception(ValueError(err_message))
continue
raw_days[day] = {
"Power": static_df.loc[selected_timestamp, "Power"],
"Speed": static_df.loc[selected_timestamp, "Speed"],
"Mode": static_df.loc[selected_timestamp, "Mode"],
"Torque": static_df.loc[selected_timestamp, "Torque"],
"Timestamp": selected_timestamp,
}
logger.debug(
f"{obj_name}: Selected moment for day {day}: {raw_days[day]} with active power {selected_power}",
)
# reading each raw file and keeping only the data for the selected moments
for raw_file in raw_files:
# getting name of raw data
raw_data_name = raw_file.split("_", maxsplit=3)[1] + "_" + raw_file.split("_", maxsplit=3)[2]
# converting name to snake case
raw_data_name = raw_data_name.replace(" ", "_").lower()
# getting the raw data def for this raw data
raw_data_name_db = f"ge_cms_{raw_data_name}"
if raw_data_name_db not in raw_data_def:
err_message = f"{obj_name}: Raw data {raw_data_name_db} not found in database."
logger.error(err_message)
errs_obj = errs_obj.add_exception(ValueError(err_message))
continue
# checking if raw_file is empty
if Path(obj_dir, raw_file).stat().st_size == 0:
logger.warning(f"{obj_name}: Raw file {raw_file} is empty. Deleting file.")
ftp_handler.delete_file(raw_file)
continue
# reading raw file
raw_df = pd.read_csv(
Path(obj_dir, raw_file),
sep=",",
decimal=".",
header=None,
engine="pyarrow",
dtype_backend="pyarrow",
parse_dates=True,
index_col=0,
date_format="%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p",
)
# dropping rows that are not in the selected moments
raw_df = raw_df[raw_df.index.isin([x["Timestamp"] for x in raw_days.values() if x is not None])].copy()
raw_df = raw_df.T
# first dropping rows with all NaNs
raw_df = raw_df.dropna(how="all")
# now dropping columns that have more than 10% of NaNs
cols_before = len(raw_df.columns)
raw_df = raw_df.dropna(axis=1, thresh=int(0.9 * len(raw_df)))
cols_after = len(raw_df.columns)
if cols_before != cols_after:
logger.warning(
f"{obj_name}: Raw file {raw_file} had {cols_before - cols_after} timestamps with more than 10% of NaNs. They were removed",
)
# converting any remaining NaNs to 0 to avoid errors in the next steps
raw_df = raw_df.fillna(0)
# converting to float 32
raw_df = raw_df.astype("float32")
# creating dict in the format to be inserted in the database
raw_data_dict = {obj_name: {raw_data_name_db: {}}}
for timestamp in raw_df.columns:
# converting column values to a numpy array
raw_data_dict[obj_name][raw_data_name_db][timestamp] = {
"value": raw_df[timestamp].to_numpy(),
"metadata": {
k: None if pd.isna(v) else v for k, v in raw_days[timestamp.date()].items() if k != "Timestamp"
},
}
# inserting data into the database
perfdb.rawdata.values.insert(data=raw_data_dict, on_conflict="update", value_as_path=False)
# deleting raw file
ftp_handler.delete_file(raw_file)
# deleting static file
ftp_handler.delete_file(static_files[0])
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(f"Error processing object {obj_name}")
# adding error to the ErrorObject
errs_obj = errs_obj.add_exception(e)
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(f"Error processing data source {ds_name}")
# adding error to the ErrorDataSource
errs_ds = errs_ds.add_exception(e)
errs_ds = errs_ds.add_exception(e)
return errs_summary
Glossary¶
The following terms are used in the variables exported by the Farm Client. This was extracted from the software help and brought here for easier access.
- Assembly Phase Passage Frequency: When a pinion and gear mesh, specific teeth contact. After rotations, these same teeth meet again, creating this frequency.
- Ball Spin 1X Frequency: An individual rolling element's rotational speed. Defects cause a one-per-turn disturbance.
- Ball Spin 2X Frequency: Twice an individual rolling element's rotational speed. Defects cause disturbances on both races, resulting in a 2X ball spin frequency component.
- Bias: The transducer bias voltage in volts DC.
- Cage Frequency: The frequency corresponding to one complete bearing cage revolution relative to a fixed reference.
- Corner Clip: The highest alarm indication in the corner of the Alarm icons.
- Crest Factor: The ratio of Direct and Direct RMS values. Changes indicate signal modifications like spikes or sideband harmonics.
- Cumulative Event Rate: The total number of impulse events detected over time.
- Cumulative Impulse Count: The total number of impulses detected.
- Cumulative Impulse Energy: The total energy of the detected impulses.
- Cumulative Impulse Measurement (CIM): A GE algorithm for detecting metal particles between gear teeth by monitoring impacts and their cumulative count and energy.
- Direct: Data representing the overall zero-to-peak acceleration amplitude (0.5 Hz to 10,000 Hz).
- Direct RMS: Similar to Direct but uses a root-mean-square (RMS) algorithm for signal magnitude (less sensitive to spikes).
- Dynamic Energy Index (DEI): A GE algorithm to determine vibration energy within set frequency bands, normalized for operating conditions for trending machine performance.
- Enveloping Spectrum Plot: Displays the repetition frequency of impulse events causing high-frequency machine vibration. Useful for early detection of bearing problems.
- Gearmesh 1X Mesh frequency: The rate at which tooth pairs contact as they mesh.
- Gearmesh 2X, 3X, etc. frequencies: Harmonics of the fundamental gear mesh frequency (multiples of 1X).
- High Pass Direct: Data representing the overall zero-to-peak acceleration amplitude (5 kHz to 10 kHz).
- Inner Race Ball Pass Frequency (IRBP): The frequency that rolling elements pass a point on the inner race.
- Kurtosis: A measure of whether data is peaked or flat compared to a normal distribution. Changes indicate signal waveform shape modifications.
- Outer Race Ball Pass Frequency (ORBP): The frequency that rolling elements pass a point on the outer race.
- Tower Sway: The bending and movement of the wind turbine tower due to wind loads. Measured in axial and transverse directions.
- WTG: Wind Turbine Generator